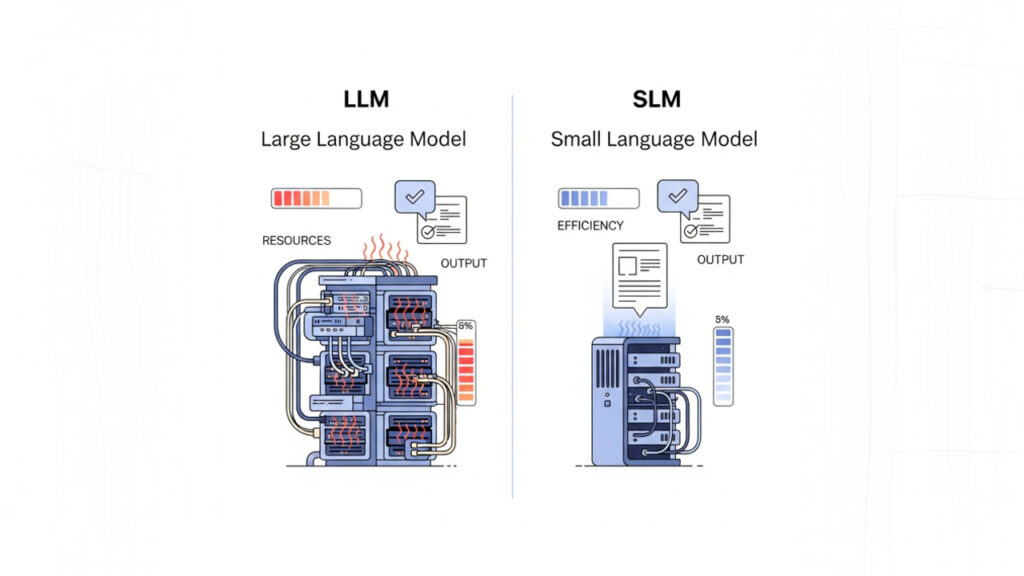
For a long time, the progress of AI was measured by one thing: the size of the models. Larger language models had very strong capabilities and soon became the center of attention in research and production environments.
However, as AI transitioned from research to practical applications, this paradigm began to reveal its shortcomings.
Very large models:
- Require large computational power
- ·Cost a lot to run
- Takes longer to respond in real-time systems
- Are more difficult to deploy in controlled environments
Due to these reasons, the attention has slowly turned to Small Language Models (SLMs).
Recent models such as Phi-3, Gemma-2, and Mistral-7B prove that size is not the determining factor of performance. With the proper approach, smaller models can be very powerful.

What Are Small Language Models
Small Language Model (SLM) – a machine learning model that aims to comprehend and produce human-like text, just like large models, but with many fewer parameters.
- Large LLMs: Usually have tens or hundreds of billions of parameters (for example, GPT-4 is approximately 1 trillion).
- Small LMs: Usually have anywhere between hundreds of millions to a few billion parameters.
Why Small Language Models Are Gaining Popularity
However, large language models are not always very practical. In most real-world applications, the full potential of large language models is simply not required.
Small language models can be applied in the following areas:
- Text summarization
- Classification
- Information retrieval
- Specific question answering
The primary reasons why organizations are shifting towards SLMs are:
- Resource efficiency
Small models can be executed on a single GPU or even on CPUs.
- Faster responses
Their smaller size enables faster inference, which is very useful in real-time applications.
- Ability for local deployment
They can be deployed locally without relying on cloud services.
- Ease of fine-tuning
Training or fine-tuning small models is much easier and faster.
Studies have revealed that with proper optimization, small models can perform equally well as large models on most task-specific benchmarks.
Privacy and Data Security Advantages
Data privacy is a significant issue, particularly in areas such as healthcare, finance, and business software.
Large models are commonly associated with cloud services, which may cause compliance and security problems.
Small language models provide a viable alternative:
- They can be executed locally
- Sensitive data is not transmitted outside the organization
- There is greater control over data access and storage
This makes SLMs appropriate for environments with strict data protection requirements.
How Small Models Still Perform Well
It is no coincidence that small models perform well. This is because there are more intelligent ways of training and optimizing models.
The key techniques are:
- Knowledge distillation – learning patterns from larger models
- LoRA and QLoRA – efficient fine-tuning by adjusting only a few parameters
- Quantization – using less memory and computation with little loss of accuracy
- High-quality training data – better data is often more important than larger models
These techniques enable small models to reason better without having to increase the size of the model.

Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
One of the biggest breakthroughs for small models is the use of retrieval-augmented generation. Rather than embedding all the knowledge inside the model:
- Relevant documents are retrieved at the time of execution
- The model responds to the question using this additional context
This helps:
- Reduce hallucinations
- Improve factual accuracy
- Small models perform well on domain-specific tasks
RAG is particularly helpful when dealing with structured or enterprise data.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Small language models are not flawless. Some problems still remain:
- Limited capabilities for long-context reasoning
- Domain change performance degradation
These problems can be addressed by:
- Improved grounding of retrieval
- Fine-tuning
- Hybrid models consisting of small and large models
The future is not about one giant model but several specialized models that can work together.
Conclusion
Small language models represent a significant paradigm shift in AI research.
Rather than concentrating solely on the scale of models, the focus has shifted to:
- Efficiency
- Deployability
- Smarter training approaches
With advancements in technology, small models will become an integral part of developing scalable, reliable, and efficient AI systems.